 If you are lucky enough to have tried bespoke tailoring in Savile Row, you will know that nothing off the rack really comes close to it. The term “bespoke” originates in Savile Row, a street in Mayfair, Central London, famous for prestigious tailoring for the individual customer. It is understood to mean that a suit is custom measured, cut and made by hand to provide a perfect fit where it literally hugs one’s body. In the world of high-end analog audio, if there is such a thing as a “bespoke tonearm,” the Primary Control tonearm from the Netherlands fits this description.
If you are lucky enough to have tried bespoke tailoring in Savile Row, you will know that nothing off the rack really comes close to it. The term “bespoke” originates in Savile Row, a street in Mayfair, Central London, famous for prestigious tailoring for the individual customer. It is understood to mean that a suit is custom measured, cut and made by hand to provide a perfect fit where it literally hugs one’s body. In the world of high-end analog audio, if there is such a thing as a “bespoke tonearm,” the Primary Control tonearm from the Netherlands fits this description.
Primary Control is an Amsterdam-based company that specializes in exquisite custom-made tonearms. Its owner, Bernd Hemmen, is an electrical engineer whose lifetime passions are music and audio. His fascination with the mechanics of turntable and tonearm design led him to create a tonearm that gives users precise management of every conceivable setup parameter, or, as he calls it, “Primary Control” over adjustability in order to allow a cartridge to retrieve signals accurately. After eight years of research and development, the Primary Control tonearm is born.
The ”bespoke” process begins with a consultation with the designer (or the dealer) about your specific turntable needs, as there really isn’t a standard model of the tonearm. The options are plentiful: 9”, 10.5” or 12” lengths; the metal parts come in matte, shiny, or black; and the armwand in carbon graphite or an exotic wood of your choice. My first review sample took a little over four months to arrive, a 12” model with a Macassar ebony armwand. A few months later, a second 10.5” model made of carbon graphite and titanium followed. The armwand is made of a titanium tube and a carbon graphite outer layer, separated by carefully inserted damping material to optimize resonant characteristics. These two arms are the first to land on North American soil.
Immediately Engaging
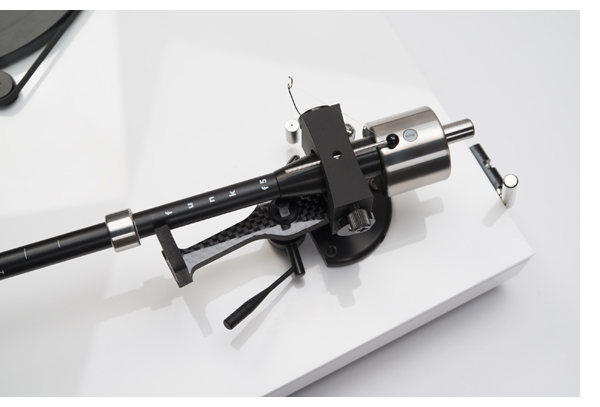
The Primary Control’s exquisite elegance can be felt right away as you unwrap the shipping box. Unlike most tonearms packed in molded Styrofoam boxes, the Primary Control is housed in a wooden box with precut foam inlays. It looks and feels expensive, reminding me of the now discontinued DaVinci Grandezza. From afar, the arm itself looks almost like a Schröder Reference tonearm with a nicer finish. The head shell mounting plate and the armwand look remarkably similar, and are both situated to the left of the mounting column.
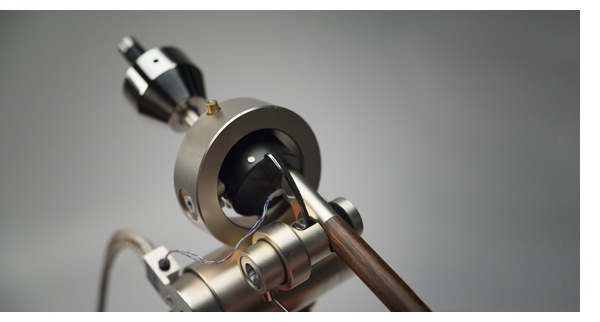
The Primary Control employs a unique proprietary two-point pivot, similar to Basis Audio’s Vector arm of the ’90s. The entire bearing structure is hidden within a round housing made of Delrin, making the bearing mechanism invisible to the naked eye. It wasn’t until I disassembled the entire bearing housing (a task not recommended by the manufacturer) that I began to understand the working mechanisms of the arm. The arm has a bearing cup mounted on the underside of armwand, which sits on a vertical sapphire bearing that points upward, based on the concept of most unipivot tonearms on which the entire armwand is balanced on a single point of contact.

Distinctly Different, Yet
Proponents of unipivot tonearms often argue that these tonearms provide a better top-end extension and a more vibrant presentation. But the free multi-directional movement of a unipivot arm is as much a nuisance as it is an advantage. Without horizontal stabilization (as in the case of the Moerch UP-4), the armwand wobbles from side to side during play resulting in measurable distortions and increased crosstalk between channels; therefore, the newer unipivot designs will have some sort of horizontal stabilization mechanism to remedy the problem. The Graham Phantom and the Durand Talea use magnetic force to stabilize the arm, whereas the Reed 3P adds on additional side bearings to restrict horizontal movements. The Primary Control incorporates a lower horizontal ball bearing into the pivot housing which makes the armwand “lean” continuously onto a right pivot, virtually eliminating side-to-side wobbling. The horizontal bearing also creates a center of gravity offset from the main pivot, which will improve stability and balance. By turning the counterweight assembly, you can adjust the “leaning force” which essentially changes the horizontal damping of the tonearm. Too much damping causes the sound to become muddy and lifeless, while too little makes the sound thin and nervous.
The instruction manual is short, concise, and filled with detailed diagrams. If one follows the 16-page manual closely to perform cartridge alignment, VTA, Azimuth, VTF, anti-skating and horizontal damping, even a novice will achieve a relatively good setup. Fortunately, some parts of the manual will tell you what sonic changes to expect with certain adjustments –– something very few owner’s manuals will do.
There are two important points which should be mentioned with regard to the mounting position of the armpost and the relative idle position of the armwand to the platter. The Primary Control is designed with the armwand situated to the left of the main column, meaning the mounting position of the main column has to be further away than normal. Both my JC Verdier La Platine and TW Raven tables require an 8” armboard to be made long rather than the normal 6” to 7”; otherwise the optimal position prescribed by the mounting template cannot be achieved on the 12” arm. The anti-skating mechanism has been carefully designed to incorporate the use of several opposing magnets to provide for a non-linear force across the record surface. If the idle position of the arm deviates too far from the template’s optional position, the antiskating force may be applied too early or too late, depending on whether the head shell position is too close or too far out relative to the platter. This is why the tonearm is “bespoke tailored” specifically for your specific turntable.
The Proof Is in the Listening
How does the arm sound? To put it simply, the ebony version is musical, elegant and soothing, whereas the graphite/titanium version is accurate, straightforward and lively.
Unlike other reviews I have written in the past in which a general sonic description can be pinned down, in this case it would be unfair to assign a blanket sonic description because every bespoke Primary Control tonearm will have sonic variations. Both arms display exceptional finesse, detail, and frequency extension which tonearms with less adjustability can only aspire to achieve. Depending on the type of music I’m playing, the seductiveness of one may draw me away from the other.
The ever-so-romantic display of poignant emotions was gracefully displayed with the 12” Macassar ebony Primary Control when the violin in the Andante in Act 3 of Delibes’s Sylvia was played (Decca SXL 6635/6, Bonynge – New Philharmonic Orchestra). Paired with the Dynavector XV-1T bamboo body cartridge, the ebony version gives a vivid display of organic qualities which are distinctively more prominent than with the graphite armwand. Though the sonic image appears more smudged and with less clearly defined edges, it makes up for the deficiency by presenting a picture which offers more human-like qualities, drawing you closer to the music.
Yet, when the grand finale in Act 3 of the same ballet is played, the graphite arm is decidedly more neutral, accurate and dynamic, but not so much as to veer towards the direction where it becomes analytical and hard sounding. It delivers a soundstage which is more upfront, yet extends further into the room. The sonic image has more three dimensional qualities. The bass goes deeper and carries more definition, texture and less boominess to the sound.
With vocal-dominant recordings ranging from 1950s Victoria de los Ángeles recordings to 2011 Adele albums, I find myself caught in the same dilemma. The ebony arm exceeds the graphite version on organic qualities, but loses out on dynamism and speediness of response. The same can be said with Fleet Foxes’ White River Hymnal, with which the graphite version offers a more upfront presentation than does the ebony version, which puts you in a few rows back. Halfway through the review, I like the arm so much I will add one of these to my reference system, but I am having difficulty in deciding which one.
The More Care, the More Sound
If there is ever a time in which the veteran can excel over the layman, the Primary Control would be the apt instrument for such a demonstration. With the meticulous attention to details and clarity in setup instructions, the layman can certainly achieve a pretty high level of sonic achievements by following setup procedures. But the Primary Control is also a tonearm which will allow a person with a bit more experience to take the sonic performance to a much higher level. Given the numerous bespoke customizable configurations available, combined with the precise adjustability of the Primary Control, it is a tonearm which offers limitless potential –– and you can be sure it will never be the bottleneck of any analog setup.
There is always a downside to anything elegant and exclusive. Just like the bespoke suits of Savile Row, the Primary Control comes with an elegant price tag. The price ranges from around $5,500 to approximately $8,000, depending on the configuration. Ten years ago, if I were to mention an $8,000 tonearm, it would likely have raised some eyebrows. But in 2014, where a slurry of new tonearm models have gone past the $10,000 mark, such as the Graham Elite, Triplanar Mk VII, or the Vertere Reference –– just to name a few –– they do make this bespoke work of art appear less exorbitant. -Richard. H. Mak
Primary Control Tonearm
MSRP: Starting at $5,500










 Color but not colored
Color but not colored Speaking of magic
Speaking of magic The Durand Talea Tonearm
The Durand Talea Tonearm Wow Factor
Wow Factor Funk Firm’s “Think of [the FX•R] as a Ford Cosworth or an AMG Mercedes” pitch repeatedly comes to mind during listening sessions. With direct comparisons via MoFi’s recent remasters of James Taylor’s JT and Rod Stewart’s Gasoline Alley, the FX•R always digs deeper into the music, not only painting a bigger sound space but rewarding with more decay and bits of information obscured by the other setup. Isn’t this what it’s all about for maniacal audiophiles?
Funk Firm’s “Think of [the FX•R] as a Ford Cosworth or an AMG Mercedes” pitch repeatedly comes to mind during listening sessions. With direct comparisons via MoFi’s recent remasters of James Taylor’s JT and Rod Stewart’s Gasoline Alley, the FX•R always digs deeper into the music, not only painting a bigger sound space but rewarding with more decay and bits of information obscured by the other setup. Isn’t this what it’s all about for maniacal audiophiles?